Five factors to consider before picking an MPLS service provider
In today’s hyper-connected and fast-paced global marketplace, connectivity is the lifeblood needed to keep businesses running smoothly. Enterprise, small or large, need reliable and fast communication networks to work and grow.
Organizations are given access to a communication network that is entirely dependable, quick, flexible, and cost effective due to MPLS and its “labelling protocol” Businesses are considering shifting to MPLS networks due to the clear advantages of MPLS connectivity, However, choosing an MPLS service provider can be time-consuming and complicated given the industry’s diverse offerings and management methods.
There are criteria that needs to be taken into consideration while evaluating the various telecom service providers to choose the most suitable solution for your businesses.
The first element that businesses need to check is the network coverage offered by the service provider. It is critical to confirm that the network carrier’s service area includes all your targeted locations, and if global connectivity is required, the network service can provide reliable international coverage. Therefore, latency, jitter, resilience, and cost of the MPLS network are all directly impacted by the service providers’ reach and coverage.
The second criteria is to consider the Network Project Management and Monitoring, because complex networks require constant management to run smoothly. Proactive management can result in reduced expense, fewer outages, and enhanced security. Therefore, the specifics of pricing and the range of services offered under the heading of network management and monitoring services must be understood by businesses.
In order to free up IT employees, it is also crucial to check whether the service provider monitors the entire network and provides managed services.
The third criteria to be mindful about while choosing an MPLS service provider is their Network Security. Security capabilities of the MPLS service provider need to be scrutinized closely. Businesses need to ensure that service providers can support and monitor the entire network closely and provide access to a dedicated security infrastructure, including experienced NOC engineers to ensure guaranteed uptime.
Another sure-fire way to assess the capabilities of the service provider is to check the SLAs (Service Level Agreements) offered. While experienced service providers with tested capabilities are usually willing to back their services with SLAs, it pays off to compare SLAs of several MPLS network providers. It is also helpful to look at their existing clients and check references to evaluate their performance.
Subsequent to comparing SLA’s, it is important for businesses to assess, evaluate and understand the Class of Service (CoSs) and Quality of Service (QoS) offered by the carrier. The Quality of Service (QoS) is impacted by the carrier’s consolidation and prioritisation decisions for different traffic categories. These standards must comply with the requirements of your business, and the contract with the service provider must specifically describe and list these service commitments.
While the mentioned points form a base to shortlist the right MPLS network provider, other factors such as routing protocols, staff expertise, 3rd party partnerships, network architecture and future scalability capabilities must also essentially be a part of the decision making process.
Despite the fact that cost is a major consideration in any business decision, your company’s long-term objectives and alignment with current and future needs should ultimately take precedence. After all, your MPLS Network will form the backbone of your business while looking at it from a wider perspective.
To Infinity and Beyond!
Vamsi Nekkanti looks at the future of data centers – in space and underwater
Data centers can now be found on land all over the world, and more are being built all the time. Because a lot of land is already being utilized for them, Microsoft is creating waves in the business by performing trials of enclosed data centers in the water.
They have already submitted a patent application for an Artificial Reef Data Center, an underwater cloud with a cooling system that employs the ocean as a large heat exchanger and intrusion detection for submerged data centers. So, with the possibility of an underwater cloud becoming a reality, is space the next-or final-frontier?
As the cost of developing and launching satellites continues to fall, the next big thing is combining IT (Information Technology) principles with satellite operations to provide data center services into Earth orbit and beyond.
Until recently, satellite hardware and software were inextricably linked and purpose-built for a single purpose. With the emergence of commercial-off-the-shelf processors, open standards software, and standardized hardware, firms may reuse orbiting satellites for multiple activities by simply downloading new software and sharing a single spacecraft by hosting hardware for two or more users.
This “Space as a Service” idea may be used to run multi-tenant hardware in a micro-colocation model or to provide virtual server capacity for computing “above the clouds.” Several space firms are incorporating micro-data centers into their designs, allowing them to analyze satellite imaging data or monitor dispersed sensors for Internet of Things (IoT) applications.

HPE Spaceborne Computer-2 (a set of HPE Edgeline Converged EL4000 Edge and HPE ProLiant machines, each with an Nvidia T4 GPU to support AI workloads) is the first commercial edge computing and AI solution installed on the International Space Station in the first half of 2021 (Image credit: NASA)
Advantages of Space Data Centers
The data center will collect satellite data, including images, and analyze it locally. Only valuable data is transmitted down to Earth, decreasing transmission costs, and slowing the rate at which critical data is sent down.
The data center might be powered by free, abundant solar radiation and cooled by the chilly emptiness of space. Outside of a solar flare or a meteorite, there would be a minimal probability of a natural calamity taking down the data center. Spinning disc drives would benefit from the space environment. The lack of gravity allows the drives to spin more freely, while the extreme cold in space helps the servers to handle more data without overheating.
Separately, the European Space Agency is collaborating with Intel and Ubotica on the PhiSat-1, a CubeSat with AI (Artificial Intelligence) computing aboard. LyteLoop, a start-up, seeks to cover the sky with light-based data storage satellites.
NTT and SKY Perfect JV want to begin commercial services in 2025 and have identified three primary potential prospects for the technology.
The first, a “space sensing project,” would develop an integrated space and earth sensing platform that will collect data from IoT terminals deployed throughout the world and deliver a service utilizing the world’s first low earth orbit satellite MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology.
The space data center will be powered by NTT’s photonics-electronics convergence technology, which decreases satellite power consumption and has a stronger capacity to resist the detrimental effects of radiation in space.
Finally, the JV is looking into “beyond 5G/6G” applications to potentially offer ultra-wide, super-fast mobile connection from space.

The Challenge of Space-Based Data Centers
Of course, there is one major obstacle when it comes to space-based data centers. Unlike undersea data centers, which might theoretically be elevated or made accessible to humans, data centers launched into space would have to be completely maintenance-free. That is a significant obstacle to overcome because sending out IT astronauts for repair or maintenance missions is neither feasible nor cost-effective! Furthermore, many firms like to know exactly where their data is housed and to be able to visit a physical site where they can see their servers in action.
While there are some obvious benefits in terms of speed, there are also concerns associated with pushing data and computing power into orbit. In 2018, Capitol Technology University published an analysis of many unique threats to satellite operations, including geomagnetic storms that cripple electronics, space dust that turns to hot plasma when it reaches the spacecraft, and collisions with other objects in a similar orbit.
The concept of space-based data centers is intriguing, but for the time being-and until many problems are worked out-data centers will continue to dot the terrain and the ocean floor.
The future of training is ‘virtual’
What sounds like the cutting edge of science fiction is no fantasy; it is happening right now as you read this article
Imagine getting trained in a piece of equipment that is part of a critical production pipeline. What if you can get trained while you are in your living room? Sounds fantastic, eh. Well, I am not talking about e-learning or video-based training. Rather what if the machine is virtually in your living room while you walk around it and get familiar with its features? What if you can interact with it and operate it while being immersed in a virtual replica of the entire production facility? Yes, what sounds like the cutting edge of science fiction is no fantasy; it is happening right now as you read this article.
Ever heard of the terms ‘Augmented Reality’ or ‘Virtual Reality’? Welcome to the world of ‘Extended Reality’. What may seem like science fiction is in reality a science fact. Here we will try to explain how these technologies help in transforming the learning experience for you.
Let’s get to the aforementioned example. There was this requirement from a major pharmaceutical company where they wanted to train some of their employees on a machine. Simple, isn’t it? But here’s the catch. That machine was only one of its kind custom-built and that too at a faraway facility. The logistics involved were difficult. What if the operators can be trained remotely? That is when Sify proposed an Augmented Reality (AR) solution. The operators can learn all about the machine including operating it wherever they are. All they needed was an iPad which was a standard device in the company. The machine simply augments on to their real-world environment and the user can walk around it as if the machine were present in the room. They could virtually operate the machine and even make mistakes that do not affect anything in the real world.
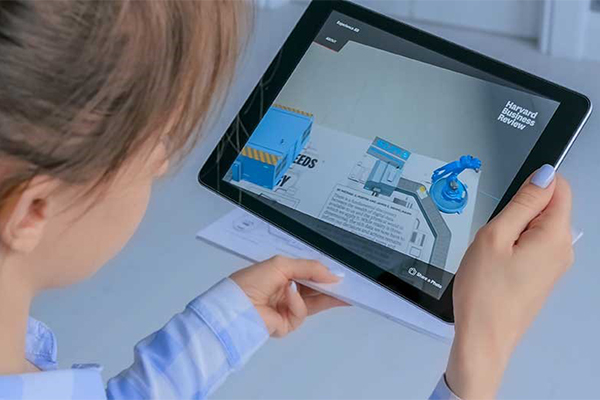

What is the point of learning if the company cannot measure the outcome? But with this technology several metrics can be tracked and analysed to provide feedback at the end of the training. So, what was the outcome of the training at the pharma company? The previous hands-on method took close to one year for the new operators to come up to speed of experienced operators. But even then, new operators took 12 minutes to perform the task that experienced operators do in 5 minutes. The gap was a staggering 7 minutes. But using the augmented reality training protocols, all they needed was one afternoon. New operators came to up speed of experienced operators within no time. This means not only can more products reach deserving patients but also significantly reduces a lot of expenditure for the company. And for the user, all they need is a smartphone or a tablet that they already have. This is an amazingly effective training solution. Users can also be trained to dismantle and reassemble complex machines without risking their physical safety.
Not only corporates but even schools can also utilise this technology for effective teaching. Imagine if the student points her tablet on the textbook and voila, the books come alive with 3D models of a volcano erupting, or even make history interesting through visual storytelling.

Now imagine another scenario. A company needs their employees to work at over 100 feet high like on a tower in an oil rig or on a high-tension electricity transmission tower. After months of training and when employees go to the actual work site, some of them realize that they cannot work at the height.

They suffer from acrophobia or a fear of heights. They would not know of this unless they really climb to that height. What if the company could test in advance if the person can work in such a setting?
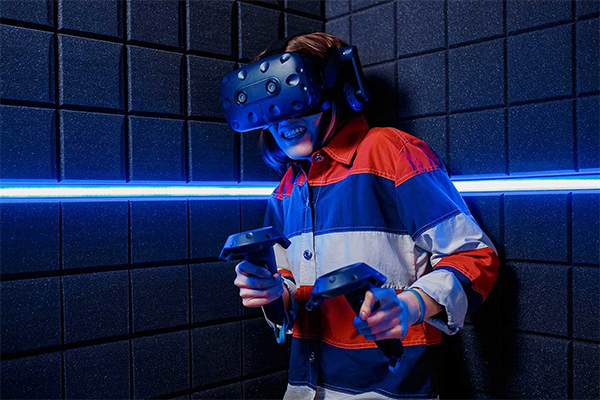

Enter Virtual Reality (VR). Using a virtual reality headset that the user can strap on to their head, they are immersed in a realistic environment. They look around and all they see is an abyss. They are instructed to perform some of the tasks that they will be doing at the work site. This is a safe way to gauge if the user suffers from acrophobia. Since VR is totally immersive, users will forget that they are safely standing on the floor and might get nervous or fail to do the tasks. This enables the company to identify people who fear heights earlier and assign them to a different task.
Any risky work environment can be virtually re-created for the training. This helps the employees get trained without any harm and it gives them confidence when they go to the actual work location.
VR requires a special headset and controllers for the user to experience it. A lot of different headsets with varying capabilities are already available for the common user. Some of these are not expensive too.
A multitude of metrics can be tracked and stored on xAPI based learning management systems (LMS). Analytics data can be used by the admin or the supervisor to gauge how the employee has fared in the training. That helps them determine the learning outcome and ROI (return on investment) on the training.
Training is changing fast and more effective using these new age technologies. A lot of collaborative learning can happen in the virtual reality space when multiple users can log on to the same training at the same time to learn a task. These immersive methods help the learner retain most of what they learnt when compared to other methods of training.
Well, the future is already here!