Sustainable Green Data Centers: How to Build Green IT Infrastructures
The rapid growth of enterprise data centers in India has led to an increasing focus on the concept of green data centers. Many businesses are now opting for alternative energy solutions for their data centers, as they offer numerous benefits. One key advantage is energy savings, which leads to cost reductions for businesses. Green data centers also contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and optimizing the use of natural resources.
Comparing India’s data statistics to global figures as of 2021, India represents 18% of the global population but has lower Internet penetration, e-commerce shopping, social media users, and mobile subscribers, all at 14%. However, India’s total mobile data traffic is significant at 113 EB, and total media traffic is 588 EB. Currently, there are 138 operational data centers in India, utilizing 737 MW power. Over the next 3-4 years, an additional 50 data centers are expected to be established, resulting in a power demand of 1050 MW. In the next 7 years, the data center consumption is projected to exceed 3000 MW of IT load demand.
This level of enormous upcoming “data center capacity” has resulted in a significant increase in the volume of energy consumption by data centers, which can have a lasting impact on the environment, and finally result in climate change.
To solve this issue, the concept of sustainable data centers has come out to reduce the environmental impact of data centers while still meeting the growing demand for digital services. As per the Green Data Center Global Market Report 2023, the global green data center market is expected to grow to $139.93 billion in 2027 at a CAGR of 19.6% for the forecasted period 2023-2027.
With this, let’s deep dive into understanding sustainable data centers, advantages of green data centers, and how to build sustainable data centers.
What Are Sustainable Data Centers?
Simply put, a sustainable data center or a green energy data center is designed and operated with a focus on environmental and social sustainability.
- Sustainability in data centers involves the implementation of a variety of practices, such as the use of renewable sources of energy like solar or wind power.
- Green data centers also help optimize energy use through efficient cooling and lighting systems, reducing water usage, and utilizing eco-friendly building materials and technologies. Green data centers also help in promoting responsible waste management practices.
Sustainable data centers strive to balance their operational needs with environmental responsibility, making significant efforts to reduce energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage while promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Advantages of Green Data Centers
Eco-friendly data centers are crucial for reducing the environmental impact of the IT industry in India. Building sustainable data centers demonstrates a company’s commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility. Here are a few benefits of Green Data Centers:
- Energy Efficiency: Green data centers employ various technologies and practices to optimize energy usage. They use energy-efficient servers, cooling systems, and power distribution mechanisms, reducing overall electricity consumption and carbon emissions.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Green data centers emit fewer greenhouse gases compared to traditional data centers. By adopting sustainable practices, they help combat climate change and contribute to global efforts to reduce carbon emissions.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Many green data centers rely on renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, or geothermal power. By harnessing clean energy, these centers decrease their reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a lower carbon footprint.
- Compliance With Environmental Regulations: Green data center solutions help companies comply with stringent government regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability.
- Cost Savings: Green energy data centers offer economic advantages by reducing energy costs and improving overall efficiency. Through energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources, green data centers can significantly lower operational costs. Over time, these savings can be substantial and may offset the initial investment in green technologies.
- Enhanced Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Companies that invest in green data centers demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. This can boost their reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers and partners.
- Longer Equipment Lifespan: Green data centers often prioritize the use of high-quality, energy-efficient hardware. This can lead to longer lifespans for servers and other equipment, reducing electronic waste and the need for frequent replacements.
- Resilience and Disaster Recovery: Most green data centers are built with redundancy and resilience in mind, reducing the risk of data loss during power outages or other emergencies. This ensures critical data remains accessible and secure.
- Leadership and Competitive Advantage: By adopting green practices, companies can position themselves as industry leaders in sustainability. This can lead to a competitive advantage as customers and investors increasingly prioritize environmentally responsible organizations.
How to Build Sustainable Data Centers?
To build sustainable data centers, companies must adopt a range of proven strategies and technologies that minimize their IT infrastructure’s environmental impact, maximize energy efficiency, and reduce carbon emissions.
- Upgrade to New Equipment: While regular maintenance and repairs can improve equipment functionality, over time, equipment becomes less reliable and more expensive to maintain. Hence, data center companies must invest in good-quality, cost-friendly data center equipment, procured from a reputed vendor. It is more advantageous in the long run to avoid the costly risk of data center downtime caused by aging and faulty equipment.
- Optimize Energy Efficiency: The first step in optimizing energy efficiency is to choose energy-efficient hardware. Proper hardware and software configuration, such as implementing power management features, is also essential for optimizing energy efficiency. Data centers must accurately measure the consumption of energy in real time and create timely alerts to keep a check on energy usage, in order to optimize energy efficiency. Identifying alternate sources of energy also helps in optimizing energy efficiency.
- Intelligent Power Management: Managing power prudently can help optimize power usage and increase energy efficiency. Through intelligent power management, predictive analytics, and efficient data center infrastructure management, a data center can maximize resource utilization, minimize energy waste, and enhance overall sustainability. Intelligent monitoring, control, and allocation of power resources within a data center infrastructure can help boost the recovery time of devices that are managed remotely.
- Virtualization: Virtualization allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server in a data center, which helps to optimize energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of multiple physical data centers. This not only improves data center resiliency but also makes a data center more sustainable.
- Using Renewable Energy Sources: Another way to reduce carbon emissions and improve sustainability is incorporating renewable energy sources into data center operations. It can involve various mechanisms like installing solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric generators. Data centers can also invest in off-site renewable energy projects, such as wind or solar farms, that can offset their energy consumption.
- Modern Cooling Systems: Several strategies to improve cooling efficiency include using free cooling systems that use outside air to cool a data center instead of traditional air conditioning. Another option is liquid cooling, which uses a liquid coolant to directly cool server components. Installing efficient airflow management mechanisms improves the effectiveness of cooling systems and reduce energy usage. Optimizing airflow is a great way to ensure sustainability and reduce operational costs in data centers.
- Implementing Automation: Automated power management tools can optimize system settings for maximum energy efficiency. Several practices, such as turning off unused devices or putting servers into low-power states during periods of low usage, can improve energy efficiency. Sustainable data centers use software-based smart design principles to optimize energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Conduct Regular Energy Audits: Regularly monitoring and assessing energy usage and carbon emissions is essential for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring data centers remain as energy efficient as possible. Conducting energy audits can provide deeper insights into energy usage patterns, identify areas for improvement, and help prioritize energy-saving initiatives.
Meeting Data Center Sustainability KPIs
Measuring and monitoring sustainability performance through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for data centers to assess their environmental impact, measure progress, and undergo continuous improvement. Some of these KPIs include:
- Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE)
- Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE)
- Carbon Usage Effectiveness (CUE)
- Server Utilization
- Recycling and Waste Management
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Compliance with Sustainability Standards
Going Green With Sify Data Centers
With over two decades of thought leadership in IT infrastructure, Sify has been delivering transformative business value to enterprises across the globe. Sify provides carbon-neutral and energy-efficient data centers by incorporating renewable energy sources, optimizing power utilization, offsetting carbon emissions, and automation through AI/ML. While ensuring sustainability, we offer high-efficiency equipment that complies with green practices like adhering to ASHRAE guidelines, implementing a carbon abatement policy, and ISO 14001 Environmental Certification.
In 2022, Sify Technologies made a commitment to renewable energy for its data center business in India. We have made power purchase agreements (PPAs) with Vibrant Energy Holdings, a majority-owned subsidiary of Blue Leaf Energy Asia Pte. Ltd. Having contracted over 230 MW of green power, Sify is successfully making progress in reducing its customers Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE)
Wrapping up!
To build a zero-carbon data center, one must follow a holistic approach that considers the entire lifecycle of the data center, right from the design and construction to ongoing operations and maintenance. By implementing a range of strategies and technologies that optimize energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions, data center operators can build green IT infrastructures that are environmentally friendly and economically sustainable.
Learn more about Sify green data centers now!
The role of data analytics and AI/ML in optimizing data center performance and efficiency
Data centers have emerged as a crucial component of the IT infrastructure of businesses. They handle vast amounts of data generated by various sources, and over the years have transformed into massive and complex entities. Of late, data analytics has emerged as a necessary ally for data center service providers, powered by the growing need to improve parameters like operational efficiency, performance, and sustainability. In this blog, we will discuss the different ways in which data analytics and AI/ML can help enhance data center management and empower data center service providers to deliver better service assurance to end-customers.
How data analytics and AI/ML can help service providers in data center optimization
Today, data center service providers are leveraging data analytics in various ways to optimize data center operations, reduce costs, enhance performance, reliability and sustainability, and improve service quality for customers. They employ a variety of methods to collect data from colocation, on-premise and edge data centers, which include physical RFID/EFC sensors, server, network and storage monitoring tools, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, configuration management databases (CMDBs), API integration, and customer usage data. The data collected is then fed into a centralized monitoring and analytics platform, which uses visualization tools, dashboards, and alert systems to analyze the data and generate insights.
Furthermore, by integrating IoT and AI/ML into data center operations, service providers are gaining deeper insights, automating various processes, and making faster business decisions. One of the most critical requirements today is for analytical tools that can help with predictive assessment and accurate decision-making for desired outcomes. This is achieved by diving deep into factors such as equipment performance, load demand curve, overall system performance, as well as intelligent risk assessment and business continuity planning. Selection of the right tools, firmware, and application layer plays a major role in making such an AI/ML platform successful.
The relationship between analytics and automation from the perspective of data centers is rather symbiotic. Data centers are already automating routine tasks such as data cleaning, data transformation, and data integration, helping data center service providers free up resources for more strategic analytics work, such as predictive modeling, forecasting, and scenario planning. In turn, data analytics provides valuable insights that enable data centers to implement intelligent automation and optimization techniques. This may include workload balancing, dynamic resource allocation, and automated incident response.
Here are some of the key areas where data analytics and automation have a significant impact:
- Enhancing operational reliability: Data analytics, AI/ML and automation can enable data centers to ensure optimal performance. This involves using predictive maintenance, studying equipment lifecycles for maintenance, and incident history analysis to learn from past experiences. In addition, AI/ML-driven vendor performance evaluation and SLA management incorporating MTTR and MTBF further strengthen operations. Leveraging these metrics within the ITIL framework helps data centers gain valuable operational insights and maintain the highest levels of uptime.
- Performance efficiency: Data centers consume a substantial amount of energy to power and maintain desirable operating conditions. To optimize services, track hotspots, prevent hardware failure, and improve overall performance, modern data centers analyze data points such as power usage, temperature, humidity, and airflow related to servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and cooling systems. Prescriptive analytics can take this a step further by providing recommendations to optimize utilization and performance.
- Predictive maintenance: Predictive analytics is a powerful technology that uses data to forecast future performance, identify and analyze risks and mitigate potential issues. By analyzing sensor data and historical trends, data center service providers can anticipate potential hardware failures and perform maintenance before they escalate, with advanced predictive analytics enabling them to improve equipment uptime by up to 20%.
- Capacity planning: Businesses today must be flexible enough to accommodate capacity changes within a matter of hours. Data center service providers also need to understand current usage metrics to plan for future equipment purchases and cater to on-demand requirements. Data analytics helps in optimizing the allocation of resources like storage, compute, and networking while meeting fluctuations in customer needs and improving agility.
- Security and network optimization: Data centers can use analytics to monitor security events and detect vulnerabilities early to enhance their security posture. By analyzing network traffic patterns, data analytics tools help identify unusual activities that may indicate a security threat. They can also monitor network performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize data routing.
- Customer insights: Data centers collect usage data, such as the number of users, peak usage times, and resource consumption, to better understand customer needs and optimize services accordingly. Analytics helps providers gain insights into customer behavior and needs, enabling them to build targeted solutions that offer better performance and value. For example, through customer-facing report generation, organizations and end-customers can gain valuable insights and optimize their operations. Additionally, analytics accelerates the go-to-market process by providing real-time data visibility, empowering businesses to make informed decisions quickly and stay ahead of the competition.
- Environment sustainability & energy efficiency: Data centers have traditionally consumed significant power, with standalone facilities consuming between 10-25 MW per building capacity. However, modern data center IT parks now boast capacities ranging from 200-400+ MW. This exponential growth has led to adverse environmental impacts, such as increased carbon footprint, depletion of natural resources, and soil erosion. Using AI/ML, performance indicators like CUE (Carbon Utilization Effectiveness), WUE (Water Utilization Effectiveness), and PUE (Power Utilization Effectiveness) are analyzed to assess efficiency and design green strategies, such as adopting renewable energy, implementing zero water discharge plants, achieving carbon neutrality, and using refrigerants with low GHG coefficients. For example, AI/ML modeling can help data centers achieve 8-10% saving on PUE below design PUE – helping to balance environmental impact with an efficiency better than what was originally planned.
- Asset and vendor performance management: The foundation of the AI/ML platform lies in the CMDB, which comprises crucial data, including asset information, parent-child relationships, equipment performance records, maintenance history, lifecycle analysis, performance curves, and end-of-life tracking. These assets are often maintained by OEMs or vendors to ensure reliability and uptime. AI/ML aids in developing availability models that factor in SLA and KPI management. It can provide unmatched visibility into equipment corrections, necessary improvements, and vendor performance. It can also help enhance project models for expansion build-outs and greenfield designs, accurately estimating the cost of POD (point of delivery) design, project construction, and delivery.
- Ordering billing and invoicing: AI/ML plays a vital role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of order, billing, and invoicing processes. Its impact spans various stages, starting from responding to RFPs to reserving space and power, managing capacity, providing early access to ready-for-service solutions, facilitating customer onboarding, and overseeing the entire customer lifecycle. This includes routine processes such as invoicing, revenue collection, order renewal, customer Right of First Refusal (ROFR) management, and exploring expansion options both within and outside the current facility.
Selecting the right data analytics solution
The implementation of data analytics and automation through AI/ML requires careful consideration as several parameters, such as data quality and level of expertise play a crucial role in delivering efficient end-results. To succeed, businesses need to choose user-friendly and intelligent solutions that can integrate well with existing solutions, handle large volumes of data, and evolve as needed.
At Sify – India’s pioneering data center service provider for over 22 years, we continuously innovate, invest in, and integrate new-age technologies like AI/ML in operations to deliver significant and desired outcomes to customers. We are infusing automation led by AI/ML in our state-of-the-art intelligent data centers across India to deliver superior customer experiences, increased efficiency, and informed decision-making, resulting in more self-sustaining and competitive ecosystems. For example, leveraging our AI/ML capabilities has been proven to lead to over 20% improvement in project delivery turnaround time. Our digital data center infrastructure services offer real-time visibility, measurability, predictability, and service support to ensure that our customers experience zero downtime and reduced Capex/Opex.
How do Sify’s AI-enabled data centers impact your business?
- Person-hour savings: Automation of customer billing data and escalations resulting in up to 300 person-hour savings in a month.
- Reduction in failures: Predictive approach for maintenance and daily checks yielding up to 20% reduced MTBF, 10% improved MTTR, and 10% reduction in unplanned/possible downtime.
- Cost savings: Improved power/rack space efficiency and savings on penalties to deliver up to 8% reduction in customer penalties by maintaining SLAs and 10% reduction in operating cost.
- Compliance adherence: Meeting global standards and ensuring operational excellence and business continuity.
To know more about our world-class data centers and how they help enterprises expect positive business outcomes, visit here.
How OTT platforms provide seamless content – A Data Center Walkthrough
With the number of options and choices available, it almost seems like there’s no end to what you can and can’t watch on these platforms. It shouldn’t be difficult for a company like Netflix to store such a huge library of shows and movies at HD quality. But the question remains as to how they provide this content to so many people, at the same time, at such a large scale?
The India CTV Report 2021 says around 70% users in the country spend up to four hours watching OTT content. As India is fast gearing up to be one of the largest consumers of OTT content, players like Netflix, PrimeVideo, Zee5 et al are competing to provide relevant and user-centric content using Machine Learning algorithms to suggest what content you may like to watch.
With the number of options and choices available, it almost seems like there’s no end to what you can and can’t watch on these platforms. It shouldn’t be difficult for a company like Netflix to store such a huge library of shows and movies at HD quality. But the question remains as to how they provide this content to so many people, at the same time, at such a large scale?
Here, we attempt to provide an insight into the architecture that goes behind providing such a smooth experience of watching your favourite movie on your phone, tablet, laptop, etc.
Until not too long ago, buffering YouTube videos were a common household problem. Now, bingeing on Netflix shows has become a common household habit. With Data-heavy and media-rich content now being able to be streamed at fast speed speeds at high quality and around the world, forget about buffering, let alone downtime due to server crashes (Ask an IRCTC ticket booker). Let’s see how this has become possible:
Initially, to gain access to an online website, the data from the origin server (which may be in another country) needs to flow through the internet through an incredulously long path to reach your device interface where you can see the website and its content. Due to the extremely long distance and the origin server having to cater to several requests for its content, it would be near impossible to provide content streaming service for consumers around the world from a single server farm location. And server farms are not easy to maintain with the enormous power and cooling requirements for processing and storage of vast amounts of data.
This is where Data Centers around the world have helped OTT players like Netflix provide seamless content to users around the world. Data Centers are secure spaces with controlled environments to host servers that help to store and deliver content to users in and around that region. These media players rent that space on the server rather than going to other countries and building their own and running it, and counter the complexities involved in colocation services.
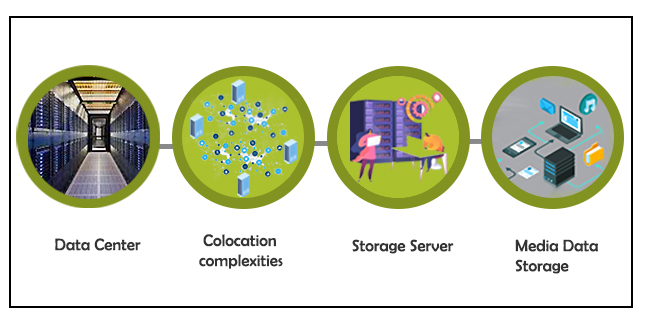
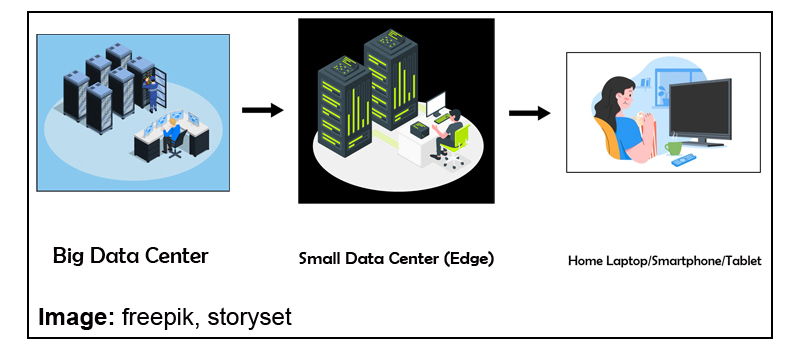
How Edge Data Centers act as a catalyst
Hosting multiple servers in Data Centers can sometimes be highly expensive and resource-consuming due to multiple server-setups across locations. Moreover, delivering HD quality film content requires a lot of processing and storage. A solution to tackle this problem are Edge Data Centers which are essentially smaller data centers (which could virtually also be a just a regional point of presence [POP] in a network hub maintained by network/internet service providers).
As long as there is a POP to enable smaller storage and compute requirements and interconnected to the data center, the edge data center helps to cache (copy) the content at its location which is closer to the end consumer than a normal Data Center. This results in lesser latency (or time taken to deliver data) and makes the streaming experience fast and effortless.
Role of Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
The edge data center therefore acts as a catalyst to content delivery networks to support streaming without buffering. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are specialized networks that support high bandwidth requirements for high-speed data-transfer and processing. Edge Data Centers are an important element of CDNs to ensure you can binge on your favorite OTT series at high speed and high quality.
Although many OTT players like Sony/ Zee opt for a captive Data Center approach due to security reasons, a better alternative would be to colocate (outsource) servers with a service provider and even opt for a cloud service that is agile and scalable for sudden storage and compute requirements. Another reason for colocating with Service providers is the interconnected Data Center network they bring with them. This makes it easier to reach other Edge locations and Data Centers and leverage on an existing network without incurring costs for building a dedicated network.
Demand for OTT services has seen a steady rise and the pandemic, in a way, acted as a catalyst in this drive.
However, OTT platform business models must be mindful of the pitfalls.
Target audience has to be top of the list to build a loyal user base. New content and better UX (User Experience) could keep subscribers, who usually opt out after the free trial, interested.
The infrastructure and development of integral elements of Edge Data Centers are certain to take centerstage to enable content flow more seamlessly in the future that would open the job market to more technical resources, engineers and other professionals.
Hyper Scale Network
Hyperscale Networks
For the new-age infrastructure, Hyperscale means the ability of the architecture to rapidly scale up to match the increasing demand of enterprise workloads. Hyperscale infrastructure relies on high bandwidth and high availability, especially for key data center sites. In this document, we talk about Hyperscale Cloud, Data Centers and how Interconnection Networks enable a seamless connectivity bridge for executing the Hybrid Cloud Strategy.
Download whitepaper
India’s First Commercial Data Center completes 21 years in Operation
Sify’s facility at Vashi was the first of the 10 Company-owned Data Centers
Chennai, Sep 20, 2021— Sify Technologies Limited (NASDAQ: SIFY), India’s most comprehensive ICT solutions provider today announced that its Data Center at Vashi, the first commercial Data Center in India, completed 21 years of uninterrupted operations.
Sify Technologies expanded into the Data Center business in the year 2000. Sify has built and today operates 10 carrier-neutral Data Centers, currently offering more than 70 MW IT Power. Following the facility at Vashi, Sify followed up with larger capacities in Bangalore, Chennai, Airoli, Noida, Rabale, Hyderabad and Kolkata and aims to add 200 MW in the next 4 years. Through CloudCover, Sify also services a network of 49 Data Centers across India.
Delighted at this milestone achievement, Mr. Raju Vegesna, Chairman, Sify Technologies, said “Sify has pioneered and set high standards in the Data Centre space in India ever since the launch of country’s first concurrently-maintainable data center at the Infotech Park in Vashi, Mumbai in September 2000. Sify was the first to foresee the scope for Data Center as a business vertical in India and hence aggressively invested in the key markets. Today, the combined strength of our Data Centers and Network connectivity puts us in an unbeatable position to drive digital transformation across the nation.”
Mr. Kamal Nath, CEO, Sify Technologies, said “This 21st anniversary of our Vashi Data Center is testimony to Sify’s legacy in the Data Center business in India. Our data center footprint across the country powers our cloud@core philosophy and drives the Integrated Data Center solutions that we offer to our clients to help them meet their digital transformation goals.”
Key advantages/ features of Sify Data Centers
- Strong connectivity with cloud cover and cost saving with cross connects
- Leading industry SLAs supporting colocation agreements
- Carrier neutral services
- Earthquake resistant structure
- Proven capability to meet 99.982% uptime
- Connectivity from major telecom carriers
- On demand cloud and Managed hosting services
About Sify Technologies
A Fortune India 500 company, Sify Technologies is India’s most comprehensive ICT service & solution provider. With Cloud at the core of our solutions portfolio, Sify is focused on the changing ICT requirements of the emerging Digital economy and the resultant demands from large, mid and small-sized businesses.
Sify’s infrastructure comprising state-of-the-art Data Centers, the largest MPLS network, partnership with global technology majors and deep expertise in business transformation solutions modelled on the cloud, make it the first choice of start-ups, SMEs and even large Enterprises on the verge of a revamp.
More than 10000 businesses across multiple verticals have taken advantage of our unassailable trinity of Data Centers, Networks and Security services and conduct their business seamlessly from more than 1600 cities in India. Internationally, Sify has presence across North America, the United Kingdom and Singapore.
Sify, www.sify.com, Sify Technologies and www.sifytechnologies.com are registered trademarks of Sify Technologies Limited.
Forward Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The forward-looking statements contained herein are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in the forward-looking statements. Sify undertakes no duty to update any forward-looking statements.
For a discussion of the risks associated with Sify’s business, please see the discussion under the caption “Risk Factors” in the company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended March 31, 2021, which has been filed with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission and is available by accessing the database maintained by the SEC at www.sec.gov, and Sify’s other reports filed with the SEC.
For information, please contact:
Sify Technologies Limited
Mr. Praveen Krishna
Investor Relations & Public Relations
+91 44 22540777 (ext.2055)
From Legacy to the Modern-day Data Center Cooling Systems
Modern-day Data Centers provide massive computational capabilities while having a smaller footprint. This poses a significant challenge for keeping the Data Center cool, since more transistors in computer chips, means more heat dissipation, which requires greater cooling. Thereby, it has come to a point where traditional cooling systems are no longer adequate for modern Data Center cooling.
Legacy Cooling: Most Data Centers still use legacy cooling systems. They use raised floors to deliver cold air to Data Center servers, and this comes from Computer Room Air Conditioner (CRAC) units. These Data Centers use perforated tiles to allow cold air to leave from the plenum to enter the main area near the servers. Once this air passes through the server units, heated air is then returned to the CRAC unit for cooling. CRAC units have humidifiers to produce steam for running fans for cooling. Hence, they also ensure the required humidity conditions.
However, as room dimensions increased in modern Data Centers, legacy cooling systems become inadequate. These Data Centers need additional cooling systems besides the CRAC unit. Here is a list of techniques and methods used for modern Data Center cooling.
Server Cooling: Heat generated by the servers are absorbed and drawn away using a combination of fans, heat sinks, pipes within ITE (Information Technology Equipment) units.1 Sometimes, a server immersion cooling system may also be used for enhanced heat transfer.
Space Cooling: The overall heat generated within a Data Center is also transferred to air and then into a liquid form using the CRAC unit.
Heat Rejection: Heat rejection is an integral part of the overall cooling process. The heat taken from the server is displaced using CRAC units, CRAH (Computer Room Air Handler) units, split systems, airside economization, direct evaporative cooling and indirect evaporative cooling systems. An economizing cooling system turns off the refrigerant cycle drawing air from outside into the Data Center so that the inside air can get mixed with the outside air to create a balance. Evaporated water is used by these systems to supplement this process by absorbing energy into chilled water and then lowering the bulb temperature to match the temperature of the air.
Containments: Hot and cold aisle containment use air handlers to contain cool or hot air and let the remaining air out. A hot containment would contain hot exhaust air and let cooler air out while cold containment would do vice versa.3 Many new Data Centers use hot aisle containment which is considered as a more flexible cooling solution as it can meet the demands of increased density of systems.
Closed-Couple cooling: Closed-Couple Cooling or CCC includes above-rack, in-rack or rear-door heat exchanger systems. It involves bringing the cooling system closer to the server racks itself for enhanced heat-exchange.2 This technology is very effective as well as flexible with long-term provisions but requires significant investments.
Conclusion
Companies can choose a cooling system based on the cooling needs, infrastructure density, uptime needs, space factors, and cost factors. The choice of the right cooling system becomes critical when the Data Center needs to have high uptime and avoid any downtime due to energy issues.
Sify offers state of the art Data Centers to ensure the highest levels of availability, security, and connectivity for your IT infra. Our Data Centers are strategically located in different seismic zones across India, with highly redundant power and cooling systems that meet and even exceed the industry’s highest standards.
How Data Center works (and how they’re changing)
A Data Center is usually a physical location in which enterprises store their data as well as other applications crucial to the functioning of their organization. Most often these Data Centers store a majority of the IT equipment – this includes routers, servers, networking switches, storage subsystems, firewalls, and any extraneous equipment which is employed. A Data Center typically also includes appropriate infrastructure which facilitates storage of this order; this often includes electrical switching, backup generators, ventilation and other cooling systems, uninterruptible power supplies, and more. This obviously translates into a physical space in which these provisions can be stored and which is also sufficiently secure.
But while Data Centers are often thought of as occupying only one physical location, in reality they can also be dispersed over several physical locations or be based on a cloud hosting service, in which case their physical location becomes all but negligible. Data Centers too, much like any technology, are going through constant innovation and development. As a result of this, there is no one rigid definition of what a Data Center is, no all-encompassing way to imagine what they are in theory and what they should look like on the ground.
A lot of businesses these days operate from multiple locations at the same time or have remote operations set up. To meet the needs of these businesses, their Data Centers will have to grow and learn with them – the reliance is not so much on physical locations anymore as it is on remotely accessible servers and cloud-based networks. Because the businesses themselves are distributed and ever-changing, the need of the hour is for Data Centers to be the same: scalable as well as open to movement.
And so, new key technologies are being developed to make sure that Data Centers can cater to the requirements of a digital enterprise. These technologies include –
- Public Clouds
- Hyper converged infrastructure
- GPU Computing
- Micro segmentation
- Non-volatile memory express
Public Clouds
Businesses have always had the option of building a Data Center of their own, to do which they could either use a managed service partner or a hosting vendor. While this shifted the ownership as well as the economic burden of running a Data Center entirely, it couldn’t have as much of a drastic effect to due to the time it took to manage these processes. With the rise of cloud-based Data Centers, businesses now have the option of having a virtual Data Center in the cloud without the waiting time or the inconvenience of having to physically reach a location.
Hyper converged infrastructure
What hyper converged infrastructure (HCI) does is simple: it takes out the effort involved in deploying appliances. Impressively, it does so without disrupting the already ongoing processes, beginning from the level of the servers, all the way to IT operations. This appliance provided by HCI is easy to deploy and is based on commodity hardware which can scale simply by adding more nodes. While early uses that HCI found revolved around desktop virtualization, recently it has grown to being helpful in other business applications involving databases as well as unified communications.
GPU Computing
While most computing has so far been done using Central Processing Units (CPUs), the expansive fields of machine learning and IoT have placed a new responsibility on Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). GPUs were originally used only to play graphics-intensive games, but are now being used for other purposes as well. They operate fundamentally differently from CPUs as they can process several different threads in tandem, and this makes them ideal for a new generation of Data Centers.
Micro segmentation
Micro segmentation is a method through which secure zones are created in a Data Center, curtailing any problems which may arise through any intrusive traffic which bypasses firewalls or. It is done primarily through and in software, so it doesn’t take long to implement. This happens because all the resources in one place can be isolated from each other in such a way that if a breach does happen, the damage is immediately mitigated. Micro segmentation is typically done in software, making it very agile.
Non-volatile memory express
The breakneck speed at which everything is getting digitized these days is a definitive indication that data needs to move faster as well! While older storage protocols like Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) and the small computer system interface (SCSI) have been been impacting technology since time immemorial, a new technology called Non-volatile memory express (NVMe) is threatening their presence. As a storage protocol, NVMe can accelerate the rate at which information is transferred between solid state drives and any corresponding systems. In doing so, they greatly improve data transfer rates.
The future is here!
It is no secret that Data Centers are an essential part of the success of all businesses, regardless of their size or their industry. And this is only going to play a more and more important factor as time progresses. A radical technological shift is currently underway: it is bound to change the way a Data Center is conceptualized as well as actualized. What remains to be seen is which of these technologies will take center stage in the years to come.
Reliable and affordable connectivity to leverage your Data Center and Cloud investments
To know more about Sify’s Hyper Cloud Connected Data Centers – a Cloud Cover connects 45 Data Centers, 6 belonging to Sify and 39 other Data Centers, on a high-speed network…
Ensure Lower Opex with Data Center Monitoring
Data Centers are the backbone of today’s IT world. Growing business, demand that the Data Centers operate at maximum efficiency. However, building Data Centers, maintaining and running them involves a lot of operational expenses for the company. It is important for companies to look for options that can help them lower Opex for their Data Centers. Proper capacity Planning, advanced monitoring techniques, and predictive analysis can help companies to achieve these goals and help improve business growth. Real-time monitoring helps Data Center operators to improve agility and efficiency of their Data Centers and achieve high performance at a lower cost.
Today’s digital world requires constant connectivity, which in turn requires all time availability. But there could be several things that could cause outages – like overloaded circuit chip, air conditioner unit malfunction, overheating of unmonitored servers, failure of UPS (uninterrupted power supply) and power surge. So how do we ensure availability? Implementing DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management) technologies can help you improve reliability. DCIM systems monitor power and environmental conditions within the Data Center. It helps in building and maintaining databases, facilitate capacity planning and assist with change management. Real-time monitoring helps improve availability and lower Opex.
Servers and electronic devices installed in Data Centers generate a lot of heat. Overheated devices are more likely to fail. Hence, Data Centers are usually kept at temperatures similar to refrigerators. Thus most of the power in a Data Center is consumed for cooling purpose. There are various techniques and technologies that Data Center operators can implement to save energy. Recent strategies like free cooling and chiller-free Data Centers, expand the allowable temperature and humidity ranges for Data Center device operations. Implementing these strategies help save energy costs. A telecommunication giant Century Link had an electricity bill of over $80 million in 2011 which made them think of a solution to lower this cost. CenturyLink implemented a monitoring program. With this monitoring program, their engineers were able to safely raise the supply air temperatures without compromising availability and with this solution CenturyLink was able to save $2.9 million annually.
As per ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers) new guidelines, the strategies like free cooling and chiller-free Data Centers can offer substantial savings and one might expect Data Center operators would make use of these seemingly straight forward adjustments. However, as per a survey, many Data Center operators are not yet following these techniques and average server supply air temperature for the Data Center is far cooler than ASHRAE recommendations.
Most of the Data Centers are provisioned for peak loads that may occur only a few times in a year. Server utilization in most of the Data Centers is only 12-18% or may peak at 20%. However, these servers are plugged in 24x7x365. In summary, though the servers are idle they are drawing the same amount of power that other operational servers are drawing. Power distribution and backup equipment implemented in Data Centers also cause substantial energy waste. Similar to cooling strategies, most of the owners employ alternate strategies to improve power efficiency. However, most of them are on the computer side. Increasing density of the IT load per rack, with the help of server consolidation and virtualization, can offer substantial savings, not only in equipment but also in electricity and space. This is an important consideration when a Data Center is located in constrained energy supply or electricity situation in the context of high real estate prices, as in most of the urban areas.
Increasing density leads to concentrated thermal output and needs modified power requirements. The effective way to maintain continuous availability in high-density deployments is real-time monitoring and granular control of the physical infrastructure. Power proportional computing or matching power supply to compute demand is the recent innovation that few of the operators are using to improve energy efficiency. Few operators use dynamic provisioning technologies or power capping features already installed on their servers. However, raising inlet air temperatures causes the risk of equipment failure. Without an in-depth understanding of the relationship between compute demand and power dynamics, implementing power capping increases the risk of the required processing capacity not being available when required. Without real-time monitoring and management, there is a high risk of equipment failure in a Data Center.
Real-time monitoring helps businesses get critical information to manage possible risks in the Data Center. Monitoring helps improve efficiency and decrease costs, enabling businesses to have availability and saving. They can lower Opex and still maintain high availability.
With the help of Real-time monitoring, a small issue can be spotted, before it becomes a large problem. In a smart Data Center, several thousands of sensors across the facility collect the information regarding air pressure, humidity, temperature, power usage, utilization, fan speed and much more – all in real time. All this information is then aggregated, normalized and reported in a specified format to operators. This allows operators to understand and adjust controls in response to the conditions – to avoid failures and maintain availability.
Monitoring has lot many benefits. Monitoring data can be used by cloud and hosting providers to document their compliance with the service level agreements. Monitoring data allows operators to automate and optimize control of physical infrastructure. Real-time monitoring gives visibility at a macro and micro level, for businesses to improve client confidence, increase Data Center availability, energy efficiency, productivity and at the same time reduce their operational expenditures by optimizing Data Centers with the help of monitoring data.
Why Data Centers are Necessary for Enterprise Businesses
Data is the most critical asset of any organization and businesses are faced with the imminent challenges of managing and governing data while ensuring data compliance. Data management is critical for every company to improve business agility with up-to-date information available anywhere, anytime to the employees who need it most. There are entire ecosystems that grow perennially around Big Data and Data Analytics, which make enterprises aim for significantly critical tools to manage everyday data.
With businesses realizing the dynamism of what can be done with their data, they are moving on from their existing resources to well-equipped Data Centers to aid better data management. Data Centers have become top priority for businesses across the globe to measure up their IT infrastructure requirements. With this shift in addressing information, Data Centers have moved beyond being just an additional storage facility. Infact, they have emerged as a key business parameter. Here is why Data Centers are necessary for enterprise businesses.
Consolidated Leadership: As an enterprise business, you have to recognize the potential in terms of leading, managing and governing your organization. Therefore, you should consider the enterprise level IT infrastructure provided by a potential Data Center service that helps your enterprise with lesser makeshift in different parts of the business. This results in consolidated leadership, centralized management and a stable governance approach to help better business decision making, for the benefit of the entire enterprise.
Reduced Barriers: Enterprises have so many facets and managing each aspect of the business is quite demanding. With the common goal being the customer, every segment of the enterprise shares the same business processes, ideologies, investment plans and capital expenditures. But due to its enterprise nature, the business is often dispersed in terms of location, products and services. This results in lack of engaging the customer across various operations of the company. With an efficient Data Center solution for enterprise business, you can reduce barriers to internal operations that affect customer service. With a convenient data management and flow, managed hosting services offered by an expert provider, will help you strengthen your ability to engage the customer across your operations.
Higher Margins: Enterprises are increasingly recognizing the growing importance of a Data Center. Investing in a tactical Data Center solution will help enterprises avail scale cost, data security and service efficiencies. Data Center service providers enable enterprises to customize solutions as per local requirements without compromising on the elemental course of the core business process. With the expansion of business, enterprises have to take account of additional resources. But with Data Center solutions, you can leverage the technical resources promptly and cost-effectively. In addition, if you require fewer systems or less storage, your provider will simply reduce implementations as per requirement. It is one of the major reasons why enterprises go for vendors who offer services, with costs incurred as per their service usage.
Data Storage and Management: Data storage needs consistently increase in an enterprise and keeping pace with the requirement surge, Data Centers continue to push the horizons of tangible capacity. Innovative ways of data management and storage are being introduced by Data Centers that instigate more enterprises to branch out into the utilization of Cloud Computing. Data Centers as well as companies are focused on meeting data storage demands that integrate both cloud and physical storage capabilities. This shift in the technology is at the cusp of driving M&A activities resulting in exponential growth in data gathering and collaboration that further enhance the need for data storage.
Safety: Given the sheer amount of data accumulation and transaction in today’s competitive environment, data security has become the top priority of every enterprise business. It has become imperative for every company to put efficient systems in place that are not only updated frequently but also monitored regularly. Constant monitoring of the systems allow you to maintain its security as potential risks and attacks are detected at the earliest. That’s why enterprises rely on third party Data Center solutions with expertise and monitoring processes to identify risks and breaches within the required time frame to be able to deal with them effectively. Most vendors offer multi-tier infrastructure setup, to effectively secure valuable data of enterprises. Besides technological security of the data, vendors also emphasize on physical security of the Data Centers, ensuring surveillance, access management, intruder alarms and physical security systems. Moreover, quick recovery processes and data retrieval in shortest turnaround time are also offered in times of environmental disasters.
Better Growth Opportunities: Most enterprises are embracing Data Center solutions after understanding the crucial role data plays in the growth of their ventures. With the advancement, Data Centers bring in the business and technology realm. And enterprises are increasingly becoming aware of managing their company from the prospect of fetching more resources to utilize high potential and growth opportunities. Your business can leverage the scale, to dominate the market with the assistance of a competent Data Center service. All you need is a proficient vendor who can help you monitor and control your data with a robust infrastructure, by automating and integrating Data Center management.
Advantages of Integrating Cloud with traditional Data Centers
A growing number of organizations are adopting cloud computing to meet the challenges of deploying their IT services as fast as they can and addressing their dynamic work load environment there by maximising their ROIs (Return on Investments).
Across the globe companies have started to view hybrid cloud as a transformative operating model – a real game changer that presents the wealth of opportunities to businesses. The two mantras which helps you to follow while adopting this technique is Enhanced agility and Overall cost savings.
Cloud computing help’s the users to access the IT resources faster than the traditional Data Centers. It also provides improved manageability requires less maintenance. This technological service also helps the users to access the resources they need for a specific task. This not only prevents you from incurring cost for computing resources which are not in use, but, improves the operational efficiencies by reducing cost and time.
By adopting Cloud computing, businesses can rapidly integrate and deliver services across the other adopted cloud environments and thereby improving business agility so also lowering the costs. Once businesses recognize this they need to choose the cloud computing option that best fit their business requirements.
Like public cloud model, private cloud models also offer seamless access to applications and data with minimal IT support. But in private cloud the service will be offered only to a particular organization. Two common types of clouds are Integrated stack and Custom cloud. The key benefit of integrated stack is pre testing and interoperability to reduce operational risks and faster deployment time as the stack is most often delivered as a single bill of material. And the importance of custom cloud is, a modular plug & play approach that allows organizations to build cloud infrastructures in smaller increments, adding capacity when needed.
Hybrid model is a combination of public and private cloud models. Now a day’s every organization started looking and adopting it due to its cost benefit. Getting into a hybrid model and the key to success is, understanding how to get started on your hybrid cloud. First of all you need to know the integration method. The dominant strategy in creating a hybrid cloud that ties traditional Data Centers with public cloud services involves the use of a front end application. Most companies have created web based front end applications that give customers access to order entry and account management functions, for example, many companies also used front end application technologies from different vendors to assemble the elements of applications into a single custom display for end users. You can use either of these front end methods to create a hybrid cloud.
The front end application based hybrid models, the applications located in the cloud and the Data Center run normally; integration occurs at the front end. There are no new or complicated processes for integrating data or sharing resources between public and private clouds.
A business can choose from a vast array of potential organizational structures. Lateral organizations, top down organizations and other type of organizational structures can all be combined into a hybrid structure. This allows a company more flexibility in distributing work and assigning job rolls. It can also be beneficial in small businesses where there are fewer employees to manage daily operations.
Hybrid structure also helps the organization to choose Shared Mission where it creates a shared mission and allows it’s employees to work on a different projects and in different sectors. This structure creates a unified team of individuals with a common goal and different experience and interest levels. Each employee is able to perform work in the areas he/she best suited to, moving from project to project and reporting to different individuals as and when it is required.
Another example of hybrid structure is Market Disruption, through which when an organization adopts itself into a market and overcomes traditional barriers of the market such as advertising budgets that could cripple financially smaller organizations. Here considering the B2B perspective, this structure can ride the wave of market disruption to a peak of creating a massive media blitz that fuels product development and demand.
The next benefit to the hybrid organizational structure is the Massive Scale that can be reached by its use. Instead of having a top heavy, traditional structure of management and employees, a hybrid organization uses a spider web based structure involving groups of individuals, sometimes in different geographic areas, working together to accomplish shared goals. This also removes the problem of distribution pipelines slowing down access to the finished product.
Ease of maintenance is another attractive characteristic. It is because cloud computing architecture requires less hardware than distributed deployments. Fewer dedicated IT staff members are necessary to maintain the integrity of the cloud’s infrastructure particularly during peak hours.
Cloud computing also supports the real time allocation of computer power for application based on actual usage. This allows cloud operators to meet the demand of peak load hours accurately without over provisioning, increasing the clouds efficiency while freeing up additional capacity for on demand deployment. From an IT perspective, support for rapid provisioning and deployment is another attractive characteristics that appeal to growing enterprises.
Cost reductions, easier implementation & maintenance, and a better flexibility are the significant benefits of cloud deployment.
Operating costs are controlled by a good design and implementation of the same. Over the long term it is very critical to optimize both capital and operating expenses. Every industry has its own leaders, with a unique jargon and cultural conventions that B2B marketers must take into accounts.





































































